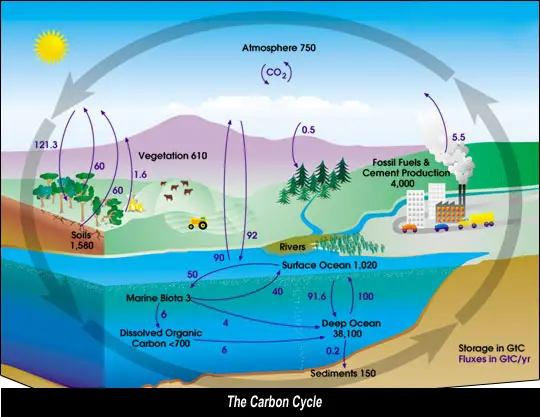
Carbon Cycle diagram:
The global carbon cycle refers to the movements of carbon, as it exchanges between reservoirs (sinks), and occurs because of various chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes. The ocean contains the largest active pool of carbon near the surface of the Earth, but the deep ocean part of this pool does not rapidly exchange with the atmosphere. Below in the diagram, you can get some idea where and how carbon is stored in the whole Earth system. The global carbon cycle is usually thought to have four major carbon sinks interconnected by pathways of exchange. These sinks are:
-the atmosphere,
-the terrestrial biosphere (which usually includes freshwater systems and non-living organic material, such as soil carbon),
-the oceans (which includes dissolved inorganic carbon and living and non-living marine biota),
-and the sediments (which includes fossil fuels ).
Carbon exists in the Earth's atmosphere primarily as the gas carbon dioxide (CO2). Although it is a very small part of the atmosphere overall (approximately 0.04% and rising fast), it plays an important role in supporting life. Other gases containing carbon in the atmosphere are methane and chlorofluorocarbons (the latter is one we introduced and are still adding to). These are all greenhouse gases whose concentration in the atmosphere are increasing, and contributing to the rising average global surface temperature.
Wednesday, February 6, 2008
Mini Project #2
Posted by Elyssa at 8:54 AM
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
0 comments:
Post a Comment